Effective communication is a crucial employability skill. Communication Skills is the first component of CBSE classes 9 and 10 Employability Skills unit of many courses such as Artificial Intelligence (417), Information Technology (402), etc. Employability Skill is a full fledged course in itself for classes 9 and 10.
At the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Discuss the various communication methods
- Provide appropriate feedback
- Gain knowledge of techniques to overcome communication barriers
- Manage stress effectively
- Develop ability to work independently
- Gain basic writing skills
Table of Contents
- What is communication
- Importance of feedback
- What is stress and how to manage it
- Working independently
- Writing skills in English
- Lesson recap
What is Communication
Communication is the ability to exchange ideas with each other. Communication must take place between two or more parties, where the party maybe a single person, an organisation or a group of people.
The person who wants to share some information is the sender while the person or group of persons who receives this information is the receiver. It is the responsibility of the sender to ensure that the information is understood completely and correctly by the receiver.
Therefore it is very important to use the correct language and keep the cultural background of the other party in mind when communicating. If you fail to make the other person understands what you want to convey, it is failure of communication.
To ensure success of communication, the sender must know what the aim of the communication is, so that he or she may ascertain that it has been effective.
Methods of communication
There are three acceptable methods of communication:
- Verbal: Communication through the use of words, be it written or spoken, is called verbal communication.
- Non-verbal: Communication through the use of signs and body language, without any use of words, is called non-verbal communication.
- Visual: Sharing of ideas and information by making others see what you want to communicate is called Visual communication.
Verbal communication

Verbal communication may occur face to face, as in meetings and personal interview, over the telephone, through letters, lectures and seminars. In the modern world, e-mail messages, chatting and video conferencing are also popular. Verbal communication is the most popular form of communication in both personal and professional lives because it enables you to share your feelings, start a relationship even with stranger, ask for help immediately and assess whether your information is being understood by the receiver or not.
Non-verbal communication
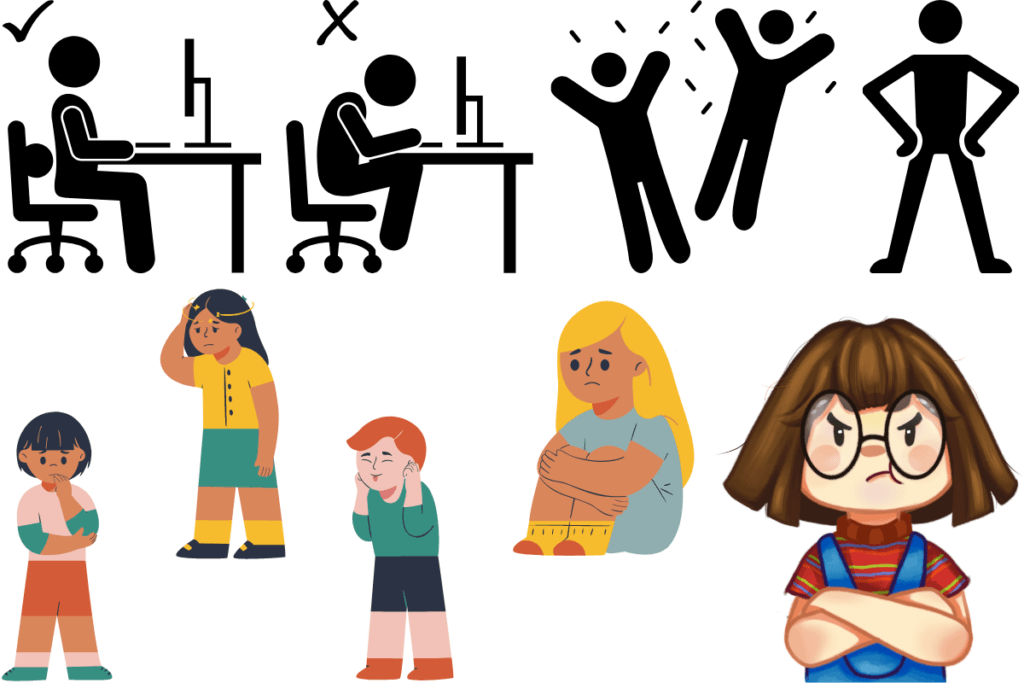
If you think you are not communicating anything while you are sitting silently, you are grossly mistaken. Despite the importance of spoken or written words during communication, importance of silence or not speaking anything cannot be underestimated.
The way you sit, the erectness of your posture, the way your hands are held, the type of dress you are wearing, your facial expressions, everything convey many things about your personality, current state of your mind, your stress levels, etc. So you must be careful even when you are not directly engaging with someone by talking.
Being silent also enables you to listen to others and understand what they want to share. As it is, your body speaks for you even when you are silent. Here are some things to keep in mind about body language:
- Always sit or stand straight, look the other person in the eyes and speak clearly. However you should take care not to stare are the other person and make them uncomfortable. Also, speaking clearly never implies speaking loudly.
- Always be properly dressed according to the occasion. For example, if you are going for a formal meeting, you must wear formal shoes besides formal dress. However if you are going out with friends for coffee you can be dressed casually. In fact you should be dressed casually so that you feel relaxed and enjoy. It has been observed that the way you dress reflects in the way you behave as well.
Visual communication
A picture is worth a thousand words. When you use images, real objects, models, charts and graphs, etc. while communicating, others can understand you better. This is so because people are able to understand better when they see something as compared to read or listen. That is why creating presentation for meetings, be it in-house or with clients, is becoming mandatory nowadays.
Communication Cycle
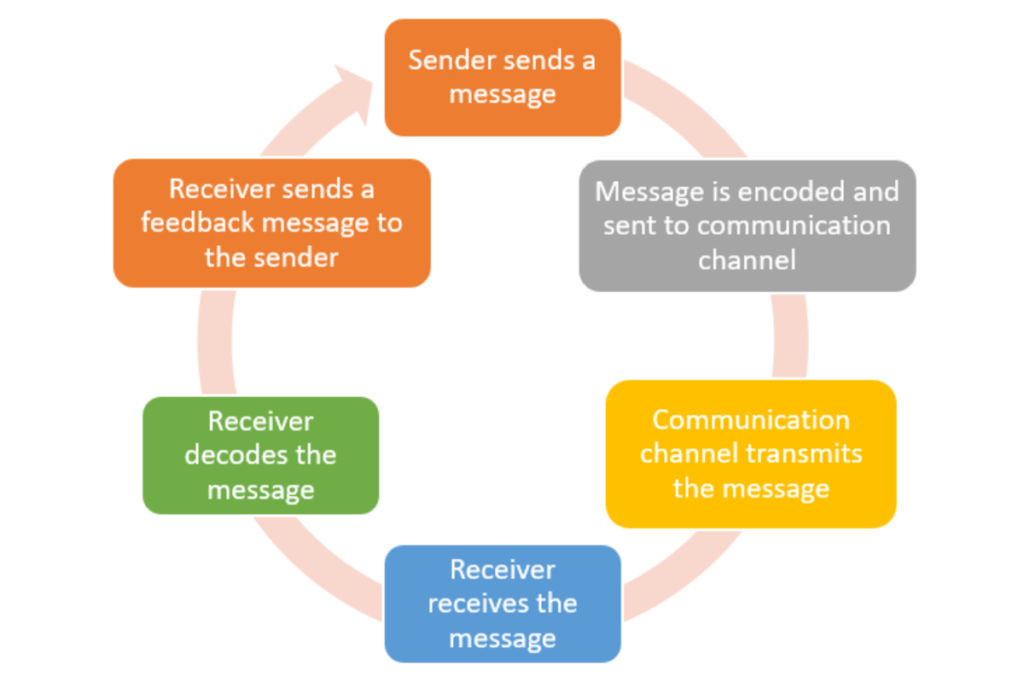
A typical communication cycle starts with a sender having ideas about what they want to communicate. This idea is converted to a concrete message in the form of an email message, PowerPoint presentation, training material, etc. (the encoding part). This message is sent through a communication channel. This channel may be the e-mail service provider, training classes, telephonic conversations, face-to-face interviews, etc. The receiver decodes this message upon receiving. After decoding the message, they give a response to the sender. The response that a receiver provides to the sender in a communication channel is called feedback. This feedback may be of these two types:
- An action or decision that needs to be taken as per the communication
- More information required for understanding the communication completely
You know that a communication is complete only when the desired action is taken.
How communication cycle plays out in real life
Let us take an example to understand this whole process. Suppose you want physics lab manual from your friend because you were absent during some physics lab period. You call up your friend on the phone and ask him to bring the manual the next day. In this whole communication, you are the sender. The request or instruction please bring your physics lab manual tomorrow to school is the message.
Upon hearing your request your friend may ask you the experiment that you want to copy from them because they want to cross check whether they have that experiment recorded in the manual or not. This is your friend’s feedback about your message. It tells you that your communication was not complete to get the desired result, that is copy a certain experiment from your friend’s physics lab manual.
In order to achieve your goal, you need to provide additional information. Ideally your original message itself should have been something like this:
I need to copy experiment 10 from your physics lab manual. If you have it please bring the manual tomorrow.
The feedback from your friend ensures that when your friend brings the manual for you they actually have the right information you want.
Importance of feedback in communication
No communication is complete without feedback because communication must always be two-way between the two parties concerned. A two-way communication means that there is exchange of ideas between the sender and the receiver. Two way communication or feedback is important due to these reasons:
- Feedback makes communication more effective by filling the gaps. If there were some things that were not missing during communication, feedback ensures that the missing information is provided to the receiver.
- Feedback is essential to make a system run in a better way. For example, when you are studying in class, if you do not tell the teacher what you are unable to understand a certain point, the teacher will not be able to explain it to you more clearly and in a different way.
- Feedback captures the receiver’s ideas, which might be valuable in improving and gaining more knowledge. For example, you have made a project for your social science exhibition. When you present the project to your tutor or even classmate, they may share their own ideas on how to improve it. Some part of their feedback might be really useful in making your project better.
Types of feedback
The feedback received or provided can be categorised in many ways, like intention of the person giving the feedback or level of detailing in the feedback. You will learn about these types of feedback here:
- Specific
- Non-specific
- Positive
- Negative
- Constructive
- Descriptive
Specific feedback
Feedback that goes into specific details like what parts are exactly good and what parts improvement how improvement could be achieved, etc. is called specific feedback. It helps the sender in understanding why his communication was effective, so that it may be repeated the next time.
Non-specific feedback
As opposed to specific feedback, some feedback are very vague and do not give any details. A feedback that only says whether the communication was good or bad, in a generic manner, is called non-specific feedback.
For example, after your drawing competition, one of the judges tells you that you are good. On the other hand another judge tells you that you are strokes were very bold or colours were very striking or the overall concept was very good. The first judge has given a non-specific feedback while the second judge has given you a specific or constructive feedback.
Positive feedback
Telling someone what they have done correctly is called positive feedback. It helps the person receiving the feedback to know what their strengths are and what activities they do well so that they may continue doing the same thing for continued success. For example, if your teacher tells you that you are good in writing essays, you will definitely attempt more long answer type questions in the exam and participate in writing competitions. If a manager tell his team member that she is good in handling people, she would volunteer for client meeting and answering customer queries in future.
Negative feedback
Telling someone about where they have gone wrong is called negative feedback. If you think that no feedback would be better than negative feedback because it may hurt someone sentiments, you are wrong. Negative feedback is much better than not getting any feedback at all. Negative feedback enables you to know what part of yourself or your performance you need to improve.
Constructive feedback
Feedback that tells you only whether you are good or bad does not help in improving yourself tangibly. Constructive feedback points out the specific area where you are good and how you can make it even better. In case of negative feedback, the person giving the feedback tells you where you went wrong and how you can improve it. This makes even negative feedback constructive and useful.
Descriptive feedback
Feedback maybe written or oral. Written feedback in the form of comments or detailed conversation discussing it is called descriptive feedback. It is more applicable to situations where a teacher or trainer is trying to make others learn something.
Have you noticed that when you submit your copies for correction to your teachers, they often write out complete answers if you have written anything wrong? If you have done something good, they write encouraging comments. This is giving descriptive feedback.
In case of a professional training, the trainer might sit with each trainee and discuss about how useful the training was to them. What were the activities or areas that the trainee found most appropriate whereas what were the areas that were boring or even irrelevant? This conversation can help both the trainer and trainee in giving and receiving feedback. If this feedback are incorporated by both the parties, the next training could be much more useful and relevant for all parties involved.
Descriptive feedback helps the learner to evaluate his or her own performance in depth.
Barriers to Effective Communication
Anything that prevents successful communication is a communication barrier. Just to remind you, a communication that achieves its goal is a successful communication. At the onset of a communication you must be aware of why you want to communicate. This “why” is the goal of your communication. Let us look at some of the most common barriers to communication.
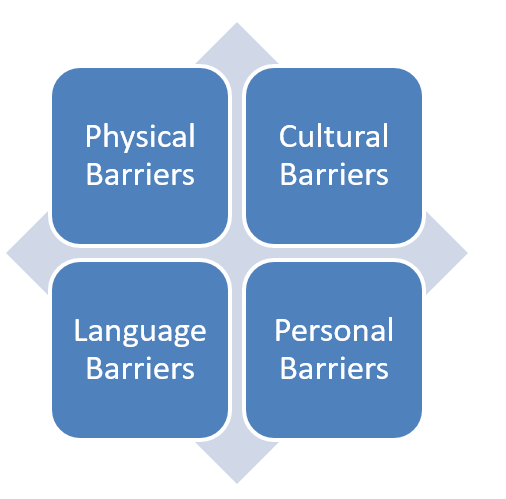
Physical barriers
The environmental condition that act as a barrier to communication between the receiver and sender is called physical barrier. Factors like noise, technical issues, etc. form the physical barrier. For example, if the microphone being used to address a large gathering of people is not functioning properly, those at the back may not be able to listen to what is being said.
Language barriers
Obstacles created during communication if the sender and receiver do not speak the same language is called language barrier. Language barrier does not pertain only to difference in language but also to difference in dialect, use of phrases, colloquial aspect of language, etc.
Cultural barriers
The problems that arise during communication due to cultural differences between the sender and the receiver is called cultural barrier. The way a person communicates with or receives communication from another person depends upon the culture to which they belong. This is because culture shapes their thinking process, body language, communication norms, etc. For example, some cultures promote looking into the eye while talking whereas some cultures take it to be rude.
Personal barriers
The barriers that are personal to the sender or the receiver and affect the successful outcome of the communication are called personal barriers. These barriers could be due to different emotional levels of maturity, past experiences, physical disabilities, etc.
Measures to overcome barriers in effective communication
Communication barriers must be removed partially or completely before any effective and successful communication may take place. Let us look at some of the ways in which the barriers discussed about may be overcome:
Be clear about what you want
You should have a very clear cut goal for your communication. Also, the message that you send out in the form of telephonic conversation, presentation, e-mail, departmental memo, training material, etc. should be very clear. You will learn more about characteristics of communication later in this lesson.
Use correct communication channel
The choice of communication channel must be correct. If you try to give lots of instructions over the phone, the receiver might not remember all of them afterwards. It is best to send list of instructions through e-mail or written memos. Similarly, if your teacher tries to teach you a concept only through smart board presentation will you be able to understand? Not necessarily. In this case it would be best to explain verbally and then use the presentation as an add-on information tool.
Use simple language while communicating
All communication, whether it is written or oral or visual, must use simple and easy to understand language. This is not the time to show off your expertise in the language. Your aim is to get the message across to the receiver.
Communicate what your audience wants
Always keep the need of your audience in mind while preparing communication material. If you try to impose your own ideas without incorporating their needs, the audience will not be receptive to your message and hence all your efforts will go waste.
Use correct body language
As you know, body language is very important in sharing your intent behind the message. So always use positive body language, do not get aggressive, never use foul language and be conscious of whether your audience is interested or not. For example, if you have written an e-mail, read it at least once to check if it is interesting till the last word. If not, the receiver would simply stop reading the message midway and your communication will fail.
Remove linguistic barriers to communication
If you are going to communicate with someone who doesn’t speak your language, you must learn the language or use an interpreter or translator. Even if you are sending message to someone in the same language it would be good if you take care of the colloquial phrases used by people living in the same geographical area as your receiver.
Get to know the receiver’s culture
If you are communicating with people of a different culture, you need to know about the cultural differences, especially with reference to body language, speaking norms, etc.
Always get feedback on your communication
Getting feedback helps you in improving your communication the next time. Do not shy away from receiving feedback because you fear you might receive a negative feedback. Even if the other person is not giving the negative feedback constructively, you should use it to identify areas that need improvement.
7 Cs of Communication
As evident from the communication cycle image, there are seven elements of the communication channel, namely, sender, ideas, encoding, communication channel, receiver, decoding, and feedback.
Basically, sender has some ideas about the messages that he wants to send the receiver. The sender uses mechanisms like writing messages, creating presentations, collecting photographs, etc. and sends it through an appropriate communication channel. This channel maybe email, telephone call, video call, conference, etc. the receiver tries to understand the message when he receives it. Then the receiver provides a feedback to the sender so that they may know that the message has been understood correctly.
Feedback helps in improving communication but it would be better if you start by framing a message that is effective.
Here you will learn how to create a message that conforms to the 7 C’s of effective communication.
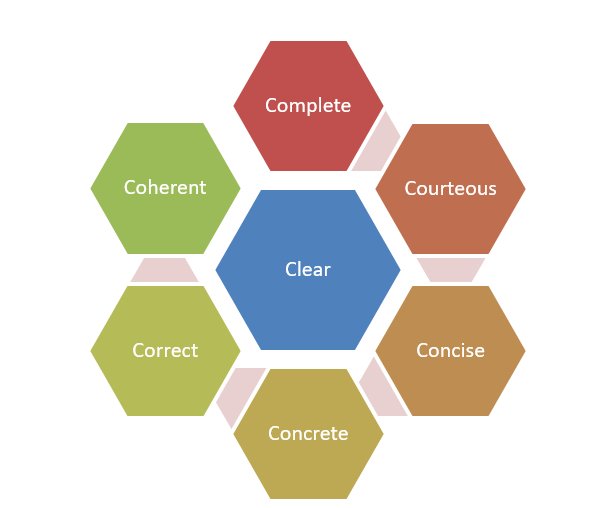
Clear
The most important aspect of any communication is that it must be easily understood. This is possible only if you are clear about what you want to communicate. If you are not sure yourself, you cannot expect the receiver to understand your ideas correctly.
Concise
You should use minimum amount of words and sentences to convey your message. Many people think that if they explain their message exhaustively the other person would be able to understand it better. However if you send a long message, whatever the communication channel, the other person is less likely to go through everything and comprehend it. You should try to keep your communication brief and to the point. For example if you share or present a PowerPoint Presentation with 42 slides in it, you are bound to lose your audience’s attention midway.
Here are some tips to create concise messages:
- Do not repeat anything again and again in different words.
- Touch upon only the fact without sharing your own perspective about them unless your perspective is important for taking a decision
Concrete
Being concise and to the point should not mean you are so cryptic that you are unable to convey your message completely. You must share the most essential points of your idea so that even the receiver is completely focused on the key points. If you do not convey all the main points about your product you are likely to lose potential customers.
Correct
You must check your message for correctness again and again before sharing it. Here correctness includes use of right vocabulary, no grammatical errors, no errors in names and salutations, and use of the right technical terms according to audience’s level of understanding. If you do not communicate correctly, the receiver will be biased against your communication even in future. So incorrect communication not only affects your current message but your future messages as well.
Coherent
The message that you are trying to convey must be coherent. It means that all the ideas present in it should be logically related and present a unified single idea. If you try to convey too many messages together, the audience or the receiver may get confused. This is especially applicable when you are writing emails or creating reports. Each sentence must relate to the previous one as well as the next one logically. You should try to keep one message for one topic. If you must include more than one topics, you must make it clear that now you would be touching upon another topic which is not entirely related to the first one.
Complete
The message you send must have all the information that the receiver might need to take an action or make a decision. For example if you are advertising a product, you must explicitly mention what you want your audience to do – buy the product, send an email or an SMS, login to their website to participate in some competition, etc.
If your message is not complete, you might have to re-send messages, which can eat into your time as well and money. Complete messages also have a better chance of persuading the receiver to agree to your ideas.
Courteous
Whether you are communicating with customers, subordinates, team members, or senior management, your tone must always be courteous. You will be able to achieve more with your communication and make greater impact if your messages are free of discourteous words, insult or veiled threats.
If you are sharing feedback or an idea as a response to the other person’s prior action, you must be even more careful to speak or write with respect. Because you have a greater chance of showing your displeasure.
Here are some ways in which you can ensure courteousness in your communication:
- Emphasize on use of you rather than I or we
- Understand the other person’s perspective rather than imposing your own
- Always be positive and result oriented in your communication
- Show interest in your receiver before expecting them to show interest in what you have to convey
What is Stress and how to handle it
The pressure felt by a person due to demanding or difficult situations is called stress. Some amount of stress is necessary for preparing ourselves to deal with difficult circumstances. However, high level of stress that continues for a long period of time is unhealthy for everyone. Some of the negative effects of stress include:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Decreased performance levels
- Sleeping disorders
- Poor digestion
- Reduction in capacity to think and/or remember
- Poor communication skills
You can see that stress causes emotional, physical as well as psychological problems. So we should be able to identify stress and know how to handle it.
Stress Management
Managing a person’s stress levels by using various techniques and therapies is called stress management.

Stress Management Techniques
Stress management techniques can broadly be categorised into professional stress management and self-help. If a person’s stress levels reach dangerous proportion and do not let him or her function properly, professional stress management is required. It entails therapies given by healthcare professionals.
On the other hand, lower level of stress can be managed by the person themselves if they are aware of their own condition. This can be identified by the symptoms being shown. The effects or symptoms of stress have already been discussed above. Let us now look at some of the stress management techniques that you can use easily.
Physical exercise
Physical exercise releases hormones that help the body to fight stress. It also reduces stress symptoms like sleep disorder, low energy levels, depression, digestive disorders, etc. So physical exercise should be part of everyone’s daily routine. It is not necessary that you do exercises for an hour every day; even 15 to 20 minutes of exercises is sufficient to relieve stress.
Yoga and meditation
Stress is caused when our mind is unable to deal with the pressure to do something. This something could be securing good marks in examination, landing a good job, getting promotions, performing well, etc. Yoga and meditation calm your mind and enable you to deal with difficult and unexpected situations without coming under stress.
Taking regular breaks
Taking break from your regular environment, which is instrumental in causing stress, is essential for managing stress. You as a student should take break from your studies to go cycling with friends or play outdoor games so that the change in environment causes your mind and body to relax.
Mind you, playing on mobile and PlayStation tires your mind and body even further, so they cannot be counted as break to relieve stress. Professionals need to go on vacation once in a while so that they can forget about the pressure at work and enable their mind and bodies to relax and heal.
Enjoying with family and friends
Being sincere and hardworking, whatever your age and work profile, does not mean that you should not enjoy life with family and friends. Your friends and family help you to highlight the good things in life, so you should spend time with them to unwind and relax. For students, Board examinations are very stressful because of the pressure to perform. So they need to close their books once in a while, maybe every couple of days, and enjoy time out with their friends or family members without worrying about the coming exams.
Taking nature walks
Nature has its own way of healing your body and mind. So whenever you feel stressed, you should go out for a walk in natural surroundings like gardens and parks. A vacation in natural surroundings like hilly areas, sea beaches, villages is located deep in jungles, is supposed to be a sure shot way of managing stress. Mind you, this location could be situated very near to where you live but you have never explored them.
Working Independently
Whether you work on your own or as part of a team, you need to be able to work independently. Working independently means that you can complete the tasks assigned to you without any supervision. When you work as part of a team, you need to be able to communicate and collaborate with others to complete task assigned to your team. In a team, the work must be broken down into activities that can be completed by individual members. So even when as part of a team, eventually you have to work on your own to achieve the targets assigned specifically to you.
To work independently you need to have certain skills such as self-awareness, self-motivation and self-regulation. Let us now discuss these terms now.
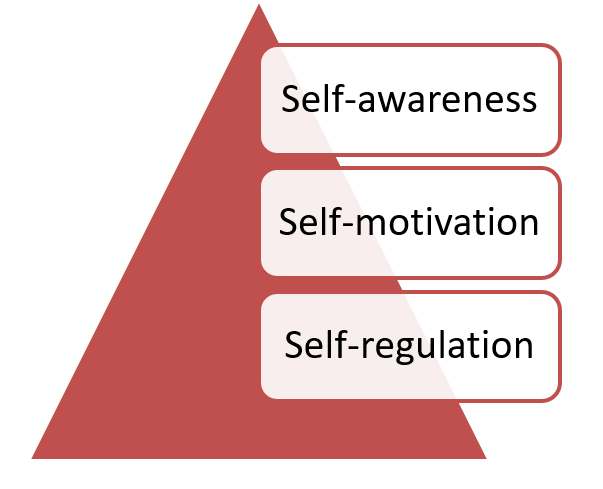
Self- awareness
Knowledge about one’s own feelings, emotions and capabilities is called self-awareness. Self-awareness is very essential to be able to work independently because it empowers you to identify what you are good at and which areas you need to improve upon. The self-aware person compares their own actions to those of their contemporaries and tries to analyse whether they are right or wrong. In this process, they are able to improve their skills, personality and performance.
As a student, you should be aware of your own strengths and weaknesses. You should know subjects that you are good at, the skills that you possess and topics that excite you. But you also need to identify the subjects where you need to work harder and skills that you need to acquire to succeed in life. When you know these things about yourself you will be able to achieve happiness and satisfaction, the ultimate aim of all human beings.
These are some of the things that you can do to increase your self-awareness about yourself:
- Write down your short term as well as long term goals. Short term goal could be achievements in your board exams whereas long term goals could be where you see yourself 5 or 10 years down the line.
- Take feedback from othere. Ask your close friends and family members to describe you. Listen to what they say attentively because they might be able to see things in you that you could not see yourself.
- Build the habit of self-reflection. Think about your actions, your choices, your feelings and emotions regularly, maybe once a week. This is called self-reflection. Self-reflection enables you to analyse your behaviour and improve it further. When you grow up you should do this every day because as an adult you do so many things, make so many choices and meet new people every day.
- Practice yoga and meditation every day. It increases your mental health, as discussed earlier, and helps you become more self-aware.
- Test yourself. You can also take personality and psychometric tests that are readily available on the Internet to access your own personality. However take care to select the established ones so that you do not end up getting wrong information about yourself. Also, always take these tests in consultation with your parents.
Self-motivation
The reason why we should do a certain task is called motivation. The ability to do what you should, without anyone else asking you to do so is called self-motivation. Whenever you do something, you always work towards a goal; you have some target to achieve, a deadline to meet or finances to manage. You must motivate yourself to meet your goals. When you are working with others or in a team, you are accountable to your team members and have to meet the team targets. These things motivate you.
However, when you work on your own, you must set your own targets and do them without anyone else monitoring you.
As a student, you must study on your own. That means, you are working independently. In certain situations you need to motivate yourself to keep studying. You could remind yourself of the target that you have set for yourself – maybe in terms of marks that you want to score, college that you want to go to or some family record that you want to break – to keep yourself motivated. Remember that you need to break down your goals into smaller achievable tasks so that you keep hitting milestones on your way to the final goal and feel motivated.
Self-regulation
Taking responsibility for one’s own learning and improvement is called self-regulation. It is most relevant in case of people who are trying to learn something. As a student you need to regulate yourself so that you can gain the required knowledge. Self-regulation has three steps:
- Doing self-study
- Monitoring the outcome of self-study
- Making changes to improve the outcome of self-study
While self-regulating your studies, you start with studying yourself from what you have been taught by your teachers as well as other study materials. Once you have studied a topic, you need to take a test to find out how much you have actually learnt. Then you need to study again to fill the gaps in your understanding.
Writing Skills in English
The first thing that you must have learnt in English was the alphabets. Alphabets are used to build words and the words are written together meaningfully to form sentences. When you want to send a written message sentences are the basic building blocks of the message. In this section we are going to look at some aspects of writing well on whatever topic given
Parts of speech
There are eight parts of speech – noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, conjunction, preposition and interjection. We will discuss each of them now.
Noun
Name of a place, person, thing, animals, etc., is called noun. For example:
Radha is going to school.
In this sentence Radha is the noun.
Pronoun
Any word a group of words that replace a noun is called a pronoun. Some examples of pronoun include he, she, it, they, we, ours, etc. Example of pronoun in a sentence:
Mohan is going to the market. He is carrying a large yellow umbrella.
Here the word he is being used in place of Mohan and hence it is a pronoun.
Adjective
Any word that describes a noun is called an adjective. In the sentence “He is carrying a large yellow umbrella” the word umbrella is also a noun and yellow is describing it. So “yellow” is an adjective
Verb
A word or group of words that show an action is called verb. In the sentence “Mohan is going to the market”, going is the action word and hence it is a verb.
Adverb
A word a group of words that tell you something more about the verb is called an adverb. For example,
Latika writes beautifully.
In the above sentence the word beautifully give me more information about the verb writes, so beautifully is an adverb of writes.
Preposition
A word that establishes a relationship between noun, pronoun or phrases with other parts of the sentence is called a preposition. Examples of prepositions are above, below, in, under, above, outside, etc.
The car is parked inside the garage.
Here the word inside is a preposition.
Conjunction
A word or group of words that joins words, phrases or sentences together is called conjunction. Examples of conjunctions – and, because, but, for, or, etc.
Example of conjunction used in a sentence:
The cat is hiding under the bed because a dog has come with the guests.
Interjection
A word or a group of words that express emotions are called interjection. Interjections are usually followed by an exclamation mark. Examples of interjection are wow, ouch, hey, oh, etc.
Example of interjection used in a sentence:
Oh! It’s so hot outside.
Parts of Sentence
Sentences have two parts – subject and predicate.
Subject contains the person, place, animal or thing that we are talking about in that sentence. It could be a noun or pronoun. Predicate is the part that contains what we are saying about that subject.
For example, look at this sentence:
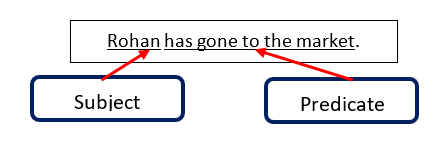
Basically the noun of the sentence is the subject and rest of the sentence forms the predicate.

Phrases
A group of words that do not form a complete sentence but have a meaning of their own are called phrases. For example, in the water, for three hours, in the park, near the gate, a dozen oranges, etc.
Features of a phrase:
- It cannot begin with a capital letter
- It does not end with the punctuation mark
- It does not make complete sense though it is meaningful
- It does not have a verb
- If you add a verb or a subject to it, it makes a complete sentence
The children are playing in the park.
Here, in the park is a phrase.

Kinds of Sentence
We categorise sentences into different kinds depending on the situation we are using them in,
For example, if you want to give an instruction to your younger brother you would say go to the market. If you are asking a question you would say are you going to the market?
This is look at the different kinds of sentences that we use
- Declarative sentences – Sentences in which you speak about a true fact or your ideas are declarative sentences. They can be both positive and negative. For example:
I like to watch movies.
The sun rises in the east. - Interrogative sentences – Sentences that ask a question are called interrogative sentences. They end with a question mark. For example:
Is that your sister?
Where do you live? - Imperative sentence – Sentences which give a command or make a request or make a suggestion are called imperative sentences. These sentences may end with a full stop or an exclamation mark. For example:
Please bring me a glass of water. (request)
You should brush your teeth twice a day. (suggestion)
You must drink milk every day. (command) - Exclamatory sentences – Sentences used to express very strong emotions are called exclamatory sentences. They always end with an exclamation mark. For example:
Wow! This is so beautiful!
My team performed fantastically!
Articles
A, an and the are called articles. They are used before nouns and used to clarify which person or thing you are referring to in a sentence.
For example,
The moon is visible at night.
A boy was going to school.
I want to eat an apple.
Here some points you should remember about articles:
- “A” and “an” can refer to indefinite things. So these are called indefinite articles. For example,
A dog is sleeping under the tree.
This is an orange. - “The” is used to refer to a particular person or thing in a sentence. So “the” is a definite article. For example, I forgot my phone at the shop.
- Definite article is not used before names of persons, languages, games, plural words, uncountable nouns, and names of plants.
Construction of Paragraph
A sequence of related sentences make a paragraph. When you have to write many things about a topic, you write in one or more paragraphs to express yourself clearly and effectively. Here are some points you must keep in mind while constructing a paragraph:
- One paragraph should have only one idea. If you move on to another idea, you should start a new paragraph.
- The first sentence of the paragraph should state the main idea. Sentences after that should support that main idea.
- All the sentences of the paragraph should be clearly understandable.
- No paragraph should really be more than half a page or 6 to 7 sentences. Long paragraphs make understanding the idea being discussed difficult.
- A paragraph should be complete in itself. If you want to break an idea into multiple paragraphs because one paragraph will be too long, you must have a single sub idea in each paragraph.
Recap of the lesson
After such a long lesson, a recap of concepts covered is in order!
- Communication is the ability to exchange ideas with each other.
- To ensure success of communication, the sender must know what the aim of the communication is.
- There are three acceptable methods of communication – verbal, non-verbal and visual.
- Communication through the use of words, be it written or spoken is called verbal communication.
- Communication through the use of signs and body language, without any use of words, is called non-verbal communication.
- Visual communication is sharing of ideas and information by making others see what you want to communicate.
- Verbal communication is the most popular form of communication in both personal and professional lives.
- The response that a receiver provides to the sender in a communication channel is called feedback.
- No communication is complete without feedback.
- Feedback that goes into specific details like what parts are exactly good and what parts improvement how improvement could be achieved, etc. is called specific feedback.
- A feedback that only says whether the communication was good or bad, in a generic manner, is called non-specific feedback.
- Telling someone what they have done correctly is called positive feedback.
- Telling someone about where they have gone wrong is called negative feedback.
- Constructive feedback points out the specific area where you are good and how you can make it even better.
- Written feedback in the form of comments or detailed conversation discussing it is called descriptive feedback.
- Anything that prevents successful communication is a communication barrier.
- The environmental condition that act as a barrier to communication between the receiver and sender is called physical barrier.
- Obstacles created during communication if the sender and receiver do not speak the same language is called language barrier.
- The problems that arise during communication due to cultural differences between the sender and the receiver is called cultural barrier.
- The barriers that are personal to the sender or the receiver and affect the successful outcome of the communication are called personal barriers.
- Communication barriers must be removed partially or completely before any effective and successful communication may take place.
- The most important aspect of any communication is that it must be easily understood.
- You should use minimum amount of words and sentences to convey your message.
- The message that you are trying to convey must be coherent.
- The message that you’re trying to convey must have all the information that the receiver might need to take an action or make a decision.
- Whether you are communicating with customers, subordinates, team members, or senior management, your tone must always be courteous.
- The pressure felt by a person due to demanding or difficult situations is called stress.
- Managing a person’s stress levels by using various techniques and therapies is called stress management.
- To work independently you need to have certain skills like self-awareness, self-motivation and self-regulation.
- Knowledge about one’s own feelings, emotions and capabilities is called self-awareness.
- The reason why we should do a certain task is called motivation.
- The ability to do what you should without anyone else asking you to do so is called self-motivation.
- Taking responsibility for one’s own learning and improvement is called self-regulation.
- There are eight parts of speech – noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, conjunction, preposition and interjection.
- Sentences have two parts – subject and predicate.
- A group of words that do not form a complete sentence but have a meaning of their own are called phrases.
- A sequence of related sentences make a paragraph.

