ICT in Our Life
ICT stands for Information and Communication Technologies. It refers to technologies that are used to store data electronically, i.e. using digital devices, and help us to use them in various fields of our lives. The most common digital device used in ICT is computers. Other devices include tablets, laptops, smartphones, etc. Wherever you go you can see computers. Whether you are in your school, visiting a hospital, bank, any office, railway station, etc. you will find computers being used every day.
OBJECTIVES
At the end of this post, you will be able to
- Discuss the uses of ICT in real life
- Identify the various components of computer system
- Identify various peripheral devices
Benefits of using computers
Do you know why computers are so omnipresent? Because they offer these advantages to users:
-
-
- They are very fast in doing their work
- They can store huge amounts of data in very small spaces
- They do not commit error even if the same work has to be repeated again and again
- They do not get bored
- They do not need to take rest if they have to work for long hours
- One computer can be used for many types of work
-
How computers assist us
Offices
Computers have made office work very easy because they can store information efficiently, in an organised way. This enables easy access of data later on.
Hospitals
In modern day hospitals, patient records are kept in computers for easy access. They are also used to operate sophisticated equipment necessary for diagnosing wide range of illnesses.
Defence
Computers are widely used in defence research. They can also be used to operate dangerous equipment, which were earlier handled by human beings.
Business
ICT is used extensively in business to enhance productivity and competitiveness. They are used for market research and demand forecasting, evaluating customers’ expectations, network with professionals and learning new skills.
Education
E-learning (electronic learning) through the use of CDs, DVDs, web-based tutorials, interactive learning software is very commonly used in schools. Internet have made it even easier for students living in remote areas to access study material as per their requirement. Now you can take online courses from any university worldwide sitting at your home. There are many courses that are free and you can use them to learn new skills.
Entertainment
Computers have affected the field of entertainment massively. Video games have got a new face with the increase in use of internet. ICT is also being used to produce music, movies and other entertainment programs to be consumed by the viewers on TV, internet and other media.
Disaster Management
Computer technologies are widely being used to predict disasters, take preventive measures and assist the victims when it strikes.
Science
Scientists have used computers for their research work since long. In fact, the initial computers were used by scientists only because they were very huge, expensive and difficult to operate. Computers today can store huge amounts of data and many new software help in accessing and analysing the data as per scientists’ requirement.
How Computers Work
Since computers are so useful to us, you must know how the computer functions. Let’s start with defining the term computer formally.
Computer is an electronic device that take some input, processes it and produces an output.
Data and Information
The input that the computer takes is called data and the output that it produces is called information. The instructions provided by the user to process the data also form the part of input. Data is also called raw facts and figures while information is also called processed data. Let’s take some examples to understand the concept of data and information.
Have you ever made tea? Or watched someone make it? What do they do? They take milk, water, sugar and tea. Then boil them together on the gas and strain the liquid to get tea. Here, milk, water, sugar and tea are the input. Boiling and straining are the processes. And the tea that is obtained is the output.
Let’s take another example.
You want to purchase a red pen for your project. So you take money from your mother, go to the market and buy the pen from a shop. Here your need for a pen and money are the input data. If your mother gave you instructions to go slowly or count the money when giving, they are also part of the input. Going to the market and purchasing are the processes that you carry out. Your pen is the output or the final product.
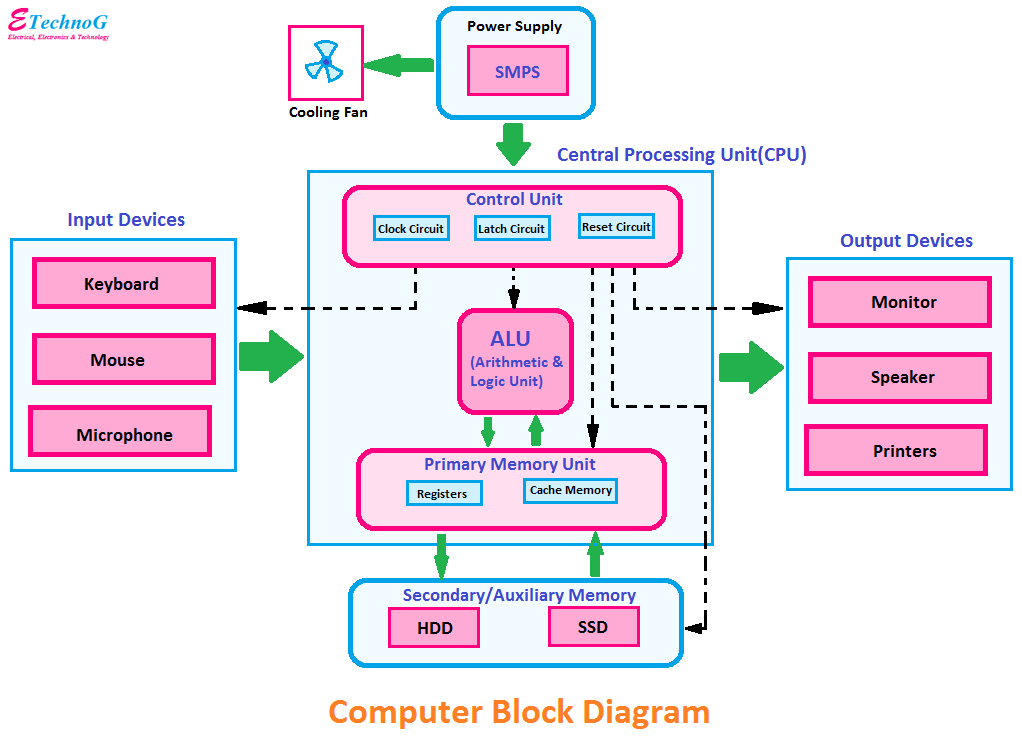
Block diagram of computer
A diagram that shows the relationship between all the units of a computer system is called the block diagram of computer.
Parts of Computer
A computer follows an input process output (IPO) cycle. To perform this cycle computer has many parts. As there are three stages in the IPO cycle, there are three categories of computer parts as well:
- Input unit – The devices that are used to give data and instructions to the computer form that input unit.
- Output unit – The devices that are used to give processed information to the user form the output unit.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU) – The devices that are used to process the given data and instructions to get the desired output form the Central Processing Unit. CPU is the brain of the computer and performs multiple tasks. It has a control unit, arithmetic logic unit and memory unit to help in performing all the processes.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
As mentioned earlier, CPU is the brain of the computer. It is responsible for processing all the data as per the instructions given by the user. It has three internal parts – ALU, CU and Memory – to enable it to perform all the functions.
Control Unit
As the name suggests, Control Unit (CU) controls all the functions of the computer. Besides the ALU and memory, the control unit is directly connected to all the devices, like input devices, output devices, storage devices, etc. You will learn about these devices later in the chapter. All devices communicate through the CU.Arithmetic Logic Unit
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the part of CPU where all arithmetic operations and logical comparisons take place. You can say that all the actual processes take place inside the ALU.
Memory
Control unit stores all the data and instructions in memory. When we say data, it includes input data, output data and data produced during the processing. When the ALU performs operations, it produces many data before the final output. For example, if you have to add three numbers, say 34, 26 and 49, your mind does something like this: 34 + 26 = 60 60 + 49 = 109 Here, 60 is the data produced during processing, or interim data. Similarly, computer also produces interim data that needs to be stored in the memory for further processing.Computer Memory Units
As you know, computer stores all the data, instructions and information in the form of 0s and 1s. These 0 and 1 are the binary digits or bits. So each bit is equal to 0 or 1. The capacity of Computer memory is measured in bytes.
1 byte = 1 B = 8 bits
Here are some higher units of Computer memory
1 Kilobyte (KB) = 1024 bytes
1 Megabyte (MB) = 1024 KB
1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1024 MB
1 Terabyte (TB) = 1024 GB
1 Petabyte (PB) = 1024 TB
Computer memory is of two types – primary memory and secondary memory. Primary and secondary memory can be further categorised, as shown here.
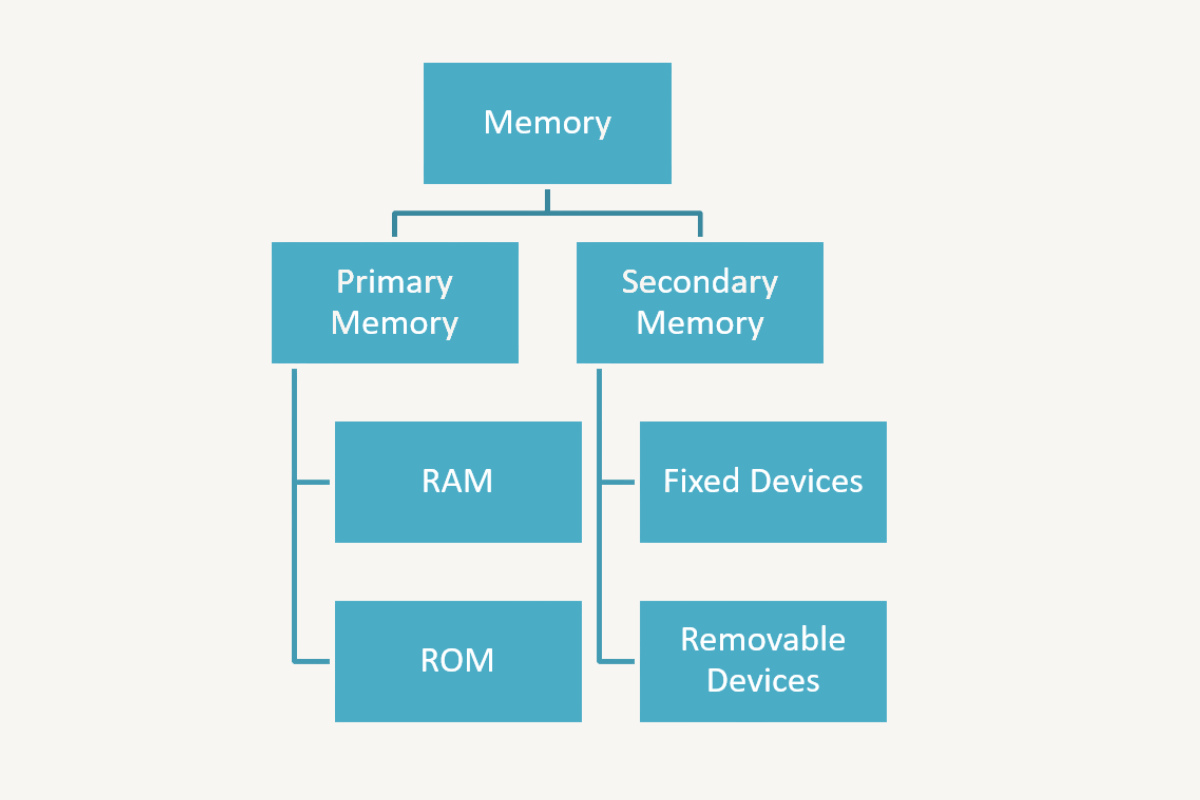
Primary Memory
The memory located inside the CPU is called Primary memory. As it is located within the CPU, it is first accessed by the CU for storing data and instructions. So, it has to be very fast. But as it is fast, it is expensive as well. These are the characteristic of primary memory:
-
- Very fast
- Very expensive
- Available in small amounts, to the tune of 2-4 GB
Primary memory is of two types:
-
- Random access memory (RAM) – Data stored on RAM gets erased when the power to the computer is switched off. When the term data is used with respect to memory storage, it implies both data and instructions. The memory that loses its data when power is switched off is called volatile memory. You can read and write to/from the RAM.
- Read only memory (ROM) – ROM is non-volatile. This means that the data stored on ROM is retained even when the computer is switched off. ROM is used to store information that does not change, like booting sequence, algorithmic tables, scientific constant values, etc. The sequence of instruction to be followed when the system is switched on, till the time you see your desktop is called booting sequence.
Secondary Memory
The memory that is located outside the CPU is called secondary memory. As the amount of primary memory is very less, secondary storage is used by the CU to store large datasets, instructions and results. These are some characteristics of secondary memory:
-
- Slower than primary memory
- Cheaper than primary memory
- Available in large quantities, to the tune of terabytes (TBs)
Secondary memory devices are also called auxilliary devices. Auxilliary devices are on two types:
-
- Fixed – The storage devices that cannot be easily removed from the computer are called fixed devices. Once they are connected to the CPU externally through wires, they always remain connected. Example of a fixed memory device is hard disk.
- Removable – The storage devices that can be easily removed from and attached to a computer are called removable devices. Example of a removable device is pen drive.
You will learn more about these storage devices in the next section.
Input Devices

As mentioned, devices used to give input to the computer system are called input devices. The two most commonly input devices are keyboard and mouse. However there are other input devices that are used for giving specific data and information to the computer. Let’s dive in.
Keyboard
Keyboard is one of the two essential input devices for a computer system. Keyboard has 104 or 108 keys. Here are the broad categories:
-
- Alphabet keys: These are the A to Z keys on the keyboard. You can type both capital and small letters using the same keys. When the caps lock key is on, you can type capital letters but if the caps lock key is off, you can type only small letters.
- Numeric keys: Numbers 0 to 9 are present as two sets of keys on the keyboard. The first set is at the top of first row of alphabet keys. The second set of numeric keys is available on the right side of the keyboard. These numeric keys are arranged together with some other keys in a square shape. This area is called the number pad. People like bankers and accountants, who have to use numbers most frequently, use this number pad as it is easier to use than the other set of numeric keys.
- Function keys: If you look at the top of your keyboard, it has keys named F1, F2, F3 till F12 at the top. These are called function keys because they provide special functionality for the application that you are using currently. For example F1 is the help key in all Microsoft software, F2 is used to save program files in C or C++, etc.
- Arrow keys: A set of four arrow keys is available to the right of the Enter key. These keys enable you to move between different lines when you are writing anything in your computer. In fact, the numeric keys of the number pad can also act as arrow keys when the num lock key is off.
- Special keys: The keys that add special function to the other keys of the keyboard are called special keys. For example, caps lock and num lock are special keys. You have just now learned how they function specially.
- Punctuation keys: Comma, period, semicolon, brackets, parenthesis and all mathematical symbols such as addition, subtraction, equal to, etc. form the punctuation keys.
- Esc key: It is used to escape or exit the current application that you are working in.
- Print screen key: You can use this key to take a photo of your screen and copy it to the clipboard. The memory of mouse is called clipboard. Once you have the image on the clipboard you can paste it anywhere like paint word, etc. And then save it.
- Home key: When you are typing in your computer using any software, you can take the cursor to the beginning of the line by pressing the home key.
- End key: When you are typing in your computer you can take the cursor to the end of any line by pressing the end key.
- Page up and page down keys: These keys can be used to shift the page up or down on the screen, one page at a time.
Mouse
Mouse is an input device that is used to select or open applications, folders and file. It is called a pointing device because an associated pointer is always visible on the screen. A mouse has two buttons and one scroll wheel. You can click or double click the mouse buttons. You can also use the drag and drop technique using the mouse. You should always keep the mouse on a mouse pad so that it performs better and has a longer life.
How to hold the mouse
To use the mouse you should put your index finger on the left mouse button, middle finger on the right mouse button and hold it with the palm. You can move the mouse in any direction with the pressure of your palm so that the mouse pointer on the screen moves.

Touchpad
As you’ve already studied a laptop has keyboard and mouse inbuilt into it. The pointing device or mouse substitute of the laptop is called touch pad. It has two buttons and a pad that is sensitive to touch. The touchpad is operated by touching the buttons and or putting pressure on the pad.Microphone
Microphone is an input device that is used to input audio data to the computer. This audio data may be in the form of voice commands or audio recordings. Microphone can be used to record your song doing voice chat, doing video chats, giving commands to the computer, etc. Microphone is attached to the computer or a laptop through the USB port.Joystick
Joystick is a special input device used for gaming. It has a stick with two spherical balls at both the ends. The upper ball is used by the player to control the joystick while the lower ball can move in all four directions. Modern gaming consoles have designer handles over this basic stick-ball-socket model describe just now. Basically a joystick points to the objects on the gaming console and moves them. A keyboard can provide the same functions but the flat design of a keyboard is not suitable for proper control. The joystick enables good hand eye coordination while using the input device.Barcode reader
Have you ever been to a grocery shop where the cashier at the cash counter scans a sticker with vertical black and white lines at the back of the product with a machine for entering product details in the billing machine? The vertical bars are called barcode. It is a unique combination of vertical black and white lines that represent product information like price, manufacturers, place of manufacturing, etc. The device used to read this barcode is called the barcode reader. The computer uses the barcode to identify the product and add it to the customer’s bill accordingly.Magnetic Ink Character Reader
Magnetic Ink Character Reader is an input device that can scan anything printed using magnetic ink. Magnetic ink is a special type of ink that has magnetic properties. The process of using magnetic ink character reader to read the magnetic characters is called magnetic ink character recognition (MICR). The most common example of MICR is bank cheques. If you look at a cheque carefully you will see a set of numbers written at its bottom. They are the magnetic ink characters and called MICR code.Optical Mark Reader
Optical Mark Reader is an input device that can read printed forms containing boxes or circles filled with a dark ink or pencil. When light is passed through this form, the device can read which boxes are filled and which are not. This technology is called Optical Mark Recognition (OMR). OMR sheets are usually used in examinations that have only multiple choice questions to be answered.
Output Devices

As discussed, devices that are used to give information to the users are called output devices. Monitor and printer are the two most commonly used output devices. But we will also study about some more output devices here.
Monitor
Monitor is the most commonly used output device used in a computer. It is also called visual display unit (VDU). It looks like a television screen and is measured in inches. Typical monitor sizes are 15 or 17 inches. Now this size is not the length or breadth of the monitor but the length of its diagonal. As laptops need to be compact, they have smaller monitors of normally 13.5 inches.
Printer
Printer is another commonly used output device but it is used to provide output as a printed sheet of paper. This printed output sheet is called hard copy. The output that is stored in the computer memory is called the soft copy.
LCD Projector
LCD stands for liquid crystal display. LCD projector is an output device that is used to show computer output on a huge screen. It is most commonly used for presentations during business meetings and conferences.
Auxilliary Devices

As mentioned earlier, the secondary storage devices are also called auxilliary devices. Here we will discuss some auxilliary devices.
Hard disk drive
Hard disk drive (HDD) is a fixed auxiliary device which is present inside the CPU cabinet. They are capable of storing huge amounts of data, in the range of Tera bytes. Each hard disk is a collection of circular magnetic disks arranged one over the other.
Compact disc (CD)
CDS are circular disc that can store up to 700 MB of data on circular optical discs. They are very cheap. CDs have to be inserted into CD drives that are located inside the CPU cabinet. Though CD drive is fixed inside the cabinet CDs can be inserted and removed easily. So, it is called a removable storage device.
Digital video display (DVD)
DVDs are also optical discs that can store data. However they can store up to 15 times the data held by CDs. They are used to store multimedia files like audio and video because high storage capacity is needed for that.
Pen drive
Pen drive is a portable memory device that is similar to the RAM but non-volatile. It is also called USB drive Flash Memory or key drive.
Input/Output Ports
With so many devices that can be attached to a computer, have you wondered how they are actually connected?
They are connected through Input/ Output (I/O) Ports. But before you understand about ports, you must know how a basic computer system looks like. As you know, a computer system basically has a monitor, keyboard, mouse and a CPU cabinet.
The processor, having CU, ALU and primary memory as its component, is designed on the motherboard, which is put inside the CPU cabinet. The cabinet is often called the CPU by the common users. All other I/O devices are connected to the CU through ports on motherboard. The interface between the CPU and external devices like mouse, keyboard, printer, microphone, etc. is called port.
Computer has many types of ports. The most common ones are:
-
- Serial port
- Parallel port
- PS/2 port
- VGA port
- USB port
Each device connects using a different type of port. Earlier, keyboard and mouse were connected using PS/2 port, but now USB port is used. USB port is the most common port through which even external hard drives, pen drives, etc. are also connected.
Recap
-
- ICT refers to technologies that are used to store data electronically and help us to use them in various fields of our lives.
- Computers are mainly used as data processors and analysers.
- Computer is an electronic device that take some input, processes it and produces an output.
- The input that the computer takes is called data and the output that it produces is called information.
- A computer follows an input process output (IPO) cycle.
- The devices that are used to give data and instructions to the computer form that input unit.
- The devices that are used to give processed information to the user form the output unit.
- The devices that are used to process the given data and instructions to get the desired output form the Central Processing Unit.
- A diagram that shows the relationship between all the units of a computer system is called the block diagram of computer.
- CPU has three internal parts – ALU, CU and Memory – to enable it to perform all the functions.
- Control Unit (CU) controls all the functions of the computer.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the part of CPU where all arithmetic operations and logical operations take place.
- Control unit stores all the data and instructions
- Computer memory is of two types – primary memory and secondary memory.
- The memory located inside the CPU is called Primary memory.
- The memory that loses its data when power is switched off is called volatile memory.
- The sequence of instruction to be followed when the system is switched on, till the time you see your desktop is called booting sequence.
- The memory that is located outside the CPU is called secondary memory.
- The pointing device or mouse substitute of the laptop is called touch pad.
- Monitor is the most commonly used output device used in a computer.
- The processor, having CU, ALU and primary memory as its component, is designed on the motherboard.
- The interface between the CPU and external devices like mouse, keyboard, printer, microphone, etc. is called port.
- Computer has many types of ports, like serial port, parallel port, USB port, VGA port and PS/2 port.
